VOC Air quality sensor Formaldehyde sensor
-
Price
Price on request ≥1piece
-
Model Number
TGS2602 -
Data Sheet
-
Package
Original packaging -
Specs
TGS2602 -
Quantity
- +Send Inquiry
Product Description
Features:
* High sensitivity to VOCs and odorous gases
* Low power consumption
* High sensitivity to gaseous air
contaminants
* Long life
* Uses simple electrical circuit
* Small size
Applications:
* Air cleaners
* Ventilation control
* Air quality monitors
* VOC monitors
* Odor monitors
Specifications
| Target gases |
Air contaminants (VOCs, ammonia, H2S, etc.) |
|---|---|
| Typical detection range | 1 - 30ppm of EtOH |
| Sensing principle | MOS type |
| Driving voltages |
Heater Voltage:5.0V Circuit Voltage:5.0V |
| Power consumption | 280mW |
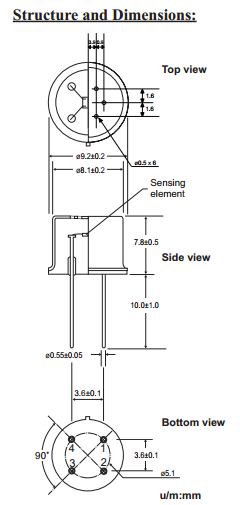
| Dimensions | φ9.2×7.8mm |
| Weight | Approx. 1.1g |
The sensing element is comprised of a metal oxide semiconductor layer formed on the alumina substrate of a sensing chip together with an integrated heater. In the presence of detectable gas, sensor conductivity increases depending on gas concentration in the air. A simple electrical circuit can convert the change in conductivity to an output signal which corresponds to the gas concentration.
The TGS 2602 has high sensitivity to low concentrations of odorous gases such as ammonia and H2S generated from waste materials in office and home
environments. The sensor also has high sensitivity to low concentrations of VOCs such as toluene emitted from wood finishing and construction products. Due to miniaturization of the sensing chip, TGS 2602 requires a heater current of only 56mA and the device is housed in a standard TO-5 package.
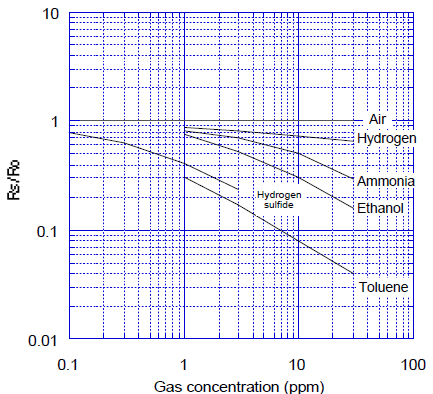
The figure below represents typical sensitivity characteristics, all data having been gathered at standard test conditions (see reverse side of this sheet). The Y-axis is indicated as sensor resistance ratio (Rs/Ro) which is defined as follows:
Rs = Sensor resistance in displayed gases at various concentrations
Ro = Sensor resistance in fresh air
Sensitivity Characteristics:
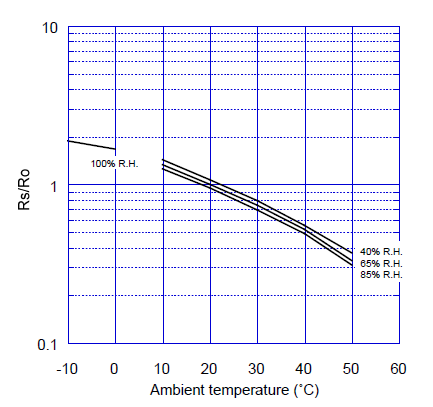
The figure below represents typical temperature and humidity dependency characteristics. Again, the Y-axis is indicated as sensor resistance ratio (Rs/Ro), defined as follows:
Rs = Sensor resistance in fresh air at various temperatures/humidities
Ro = Sensor resistance in fresh air at 20°C and 65% R.H.
Temperature/Humidity Dependency: